Install packages#
Note that hazard requires many more packages than physrisk, reflecting its role in generating indicators. There are a couple of ways to install the necessary packages. #### 1 Install using pipenv via command line (recommended)
e.g. from Elyra JupyterLab, go File -> New -> Terminal to create a new terminal, then:
cd hazard
pipenv install
2 Install using pip in notebook#
First it’s necessary to create requirements.txt from Pipfile and then install via pip:
pipenv requirements > requirements.txt
pip install -r requirements.txt
Insert bucket name and credentials as environment variables#
Need file credentials.env at top level (i.e. same level as LICENSE), containing:
[4]:
import os
import sys # noqa: E402
sys.path.append("../src")
import hazard.utilities.zarr_utilities as zarr_utilities # noqa: E402
os.environ["CREDENTIAL_DOTENV_DIR"] = os.path.dirname(os.getcwd())
zarr_utilities.set_credential_env_variables()
Run cut-down hazard indicator creation job#
[ ]:
from dask.distributed import Client, LocalCluster # noqa: E402
import logging # noqa: E402
from hazard.docs_store import DocStore # type: ignore # noqa: E402
from hazard.models.days_tas_above import DaysTasAboveIndicator # noqa: E402
from hazard.sources.nex_gddp_cmip6 import NexGddpCmip6 # noqa: E402
from hazard.sources.osc_zarr import OscZarr # noqa: E402
logging.basicConfig(
level=logging.INFO,
format="[%(asctime)s] {%(filename)s:%(lineno)d} %(levelname)s - %(message)s",
handlers=[
logging.FileHandler(filename="batch.log"),
logging.StreamHandler(sys.stdout),
],
)
docs_store = DocStore(prefix="hazard_test")
cluster = LocalCluster(processes=False)
client = Client(cluster)
gcm = "NorESM2-MM"
scenario = "ssp585"
year = 2030
source = NexGddpCmip6()
target = OscZarr(
prefix="hazard_test"
) # test prefix is "hazard_test"; main one "hazard"
# as an alternative, we can create a local target:
# test_output_dir = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "src/test/test_output")
# store = zarr.DirectoryStore(os.path.join(test_output_dir, 'hazard', 'hazard.zarr'))
# target = OscZarr(store=store)
# cut down the transform
model = DaysTasAboveIndicator(
threshold_temps_c=[15],
window_years=1,
gcms=[gcm],
scenarios=[scenario],
central_years=[year],
)
# to do the full job, simply:
# model = DaysTasAboveIndicator()
docs_store.update_inventory(model.inventory())
model.run_all(source, target, client=client)
# can also do:
# items = list(model.batch_items())
# model.run_single(items[0], source, target, client=client)
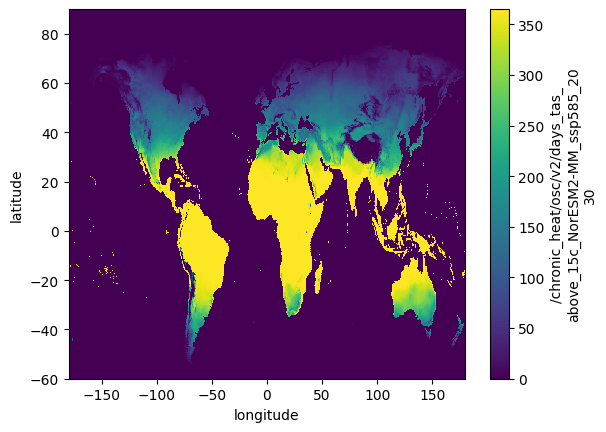
Plot one of the indicators#
[10]:
from hazard.sources.osc_zarr import OscZarr # noqa: E402
import os
import os.path # noqa: E402
target = OscZarr(prefix="hazard_test")
da = target.read("chronic_heat/osc/v2/days_tas_above_15c_NorESM2-MM_ssp585_2030")
da.plot()
[10]:
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x142ecd130>
List contents of ‘directory’#
Use s3fs to treat like directory structure, but some care needed:
s3fs caches so care needed if objects are changed outside of s3fs
Best to use boto3 client for handling large number of objects (see below)
[ ]:
import s3fs # noqa: E402
s3 = s3fs.S3FileSystem(
anon=False,
key=os.environ["OSC_S3_ACCESS_KEY"],
secret=os.environ["OSC_S3_SECRET_KEY"],
)
s3.ls(os.environ["OSC_S3_BUCKET"] + "/hazard_test/hazard.zarr")
Copy from one bucket to another bucket#
Use boto3 client and paginator for dealing with large number of objects.
[ ]:
import boto3 # noqa: E402
bucket_name = os.environ["OSC_S3_BUCKET"]
prefix = "hazard_test/hazard.zarr/chronic_heat/osc/v2"
s3_client = boto3.client(
"s3",
aws_access_key_id=os.environ["OSC_S3_ACCESS_KEY"],
aws_secret_access_key=os.environ["OSC_S3_SECRET_KEY"],
)
paginator = s3_client.get_paginator("list_objects_v2")
pages = paginator.paginate(Bucket=bucket_name, Prefix=prefix)
# get the list of keys with the given prefix
keys = []
for page in pages:
for objs in page["Contents"]:
if isinstance(objs, list):
keys.extend([obj["Key"] for obj in objs])
else:
keys.append(objs["Key"])
print(keys)
[ ]:
# Use this script to promote from hazard_test to hazard
target_bucket_name = "..."
# might be same as bucket_name
for key in keys:
copy_source = {"Bucket": bucket_name, "Key": key}
target_key = key.replace("hazard_test/hazard.zarr", "hazard/hazard.zarr")
print(f"{key} to {target_key} for bucket {bucket_name}")
s3_client.copy_object(
CopySource=copy_source, Bucket=target_bucket_name, Key=target_key
)
